1. INTRODUCTION
One of the fastest growing industries in the world today is the fast food industry with companies operating within this industry investing significant amounts of money as a way of increasing demand for the products offered. Two main factors that have prompted the substantial increase in growth for the industry are quick service and fantastic taste with the companies in this industry focusing more on research and development as a way of advancing their menus. According to Qin, Prybutok, and Zhao (2010, p.434), although the fast food menu was developed in the West, the demand for fast food products has increased significantly in different parts of the world. That has been attributed to the fact that the majority of the companies operating in this industry have been on the forefront towards advancing their investments in different markets around the world.
Some of the major companies operating in the fast food industry, which include McDonald's and Kentucky Fried Chicken (KFC) have ventured into the fast food industry in emerging markets such as China. The venturing of these two companies into emerging markets has created a significant boom in the industry considering that they have focused much of their attention towards building progressive avenues from which to capture the attention of the consumers. Additionally, this has also played a critical role in promoting knowledge of fast food products among consumers in different parts of the world. Embarking on a comparative study focusing on the fast food industry in the United Kingdom and China is essential, as it would help
in examining some of the critical differences that companies in this industry are experiencing in the two markets.
However, it is essential to take note of the fact that marketing strategies have also played a key role towards ensuring that the companies advance their positions in building that proactive position in the world today. The approaches taken as part of the marketing process tend to vary from one country to another considering that consumers tend to have varied levels of appeal towards the fast food products offered (Tan, Oriade, and Fallon, 2014, p.44). From that view, it is essential to take note of the fact that indeed fast food companies have a crucial role towards ensuring that they develop differentiated strategies that would enhance their achievement of set objectives. In that view, the focus for this study was to conduct a comparative analysis on two fast food markets, which are China and the United Kingdom with the intention of having to determine the levels of response among consumers.
On the other hand, it is essential to take note of the fact that the fast food industry has experienced a significant shift within the last few years due to a vast array of factors. An example of an element that has impacted this industry significantly is the global recession, which created a financial crisis between 2007 and 2009. However, a significant number of companies operating in the fast food industry have been able to maintain above par performance regardless of the impacts. From a general perspective, it is clear that the fast food industry has a wide array of attributes that define the overall projection of the industry each of which has been of great value toward building that positive connection to enhanced financial performance.
The focus of the study is to engage in an in-depth analysis of the fast food industry in China when compared to the same industry within the United Kingdom. The comparative analysis will focus on analyzing the development of the fast food industry in these two countries, which is essential in highlighting any significant similarities and differences. The investigation will examine how the industry, in both countries, has grown towards overcoming some of the crucial challenges that tend to impact performance for businesses. On the other hand, the analysis will seek to examine the variation in factors within these two industries with the sole focus being towards projecting an elevated level of understanding. In overall, the comparative analysis will be essential in trying to project a high level of knowledge on the growth and development of this industry in the two countries.
1.1 A rationale for the Study
The benefits projected from the growing fast food industry is one of the key factors noted as the main contributor to the high levels of investment with the number of companies operating in the sector increased significantly within the last few years. Majority of the companies operating in this industry are finding solace in emerging markets, which offer a substantial platform from which to advance their investments. Additionally, these emerging markets provide a viable platform from which to ensure that the industry maintains high standards regarding expected outcomes associated with the globalization of the industry. The consequence of this is that researchers have been on the forefront in engaging research studies that seek to provide
readers with detailed analyses on the benefits associated with the fast food industry as one of the viable avenues for investment.
The comparative case study will focus on China and the United Kingdom, which project significant differences regarding culture and food choices, thus, acting as essential choices to examine in analyzing their respective fast food industries. The differentiation between these two countries creates that viable platform from which to ensure that one can examine how the fast food industry experts to advance its position as a leading industry for investment in both countries. The comparative study seeks to create a higher level of understanding on the challenges, as well as, opportunities that fast food companies operating in both countries have experienced based on the increasing demand for their products. The study will seek to examine companies such as McDonalds and KFC both of which have entered the Asian market while operating in the United Kingdom.
1.2 Research Aim
This research aims to conduct a comparative study of the fast-food industry of China and the United Kingdom to understand the factors, which have led to growth in this industry. The study will seek to examine the fast food industries in China and the United Kingdom separately with the aim of trying to determine how each of these industries has been able to build itself. Additionally, the analysis will examine other factors including some of the critical challenges that the industry has experienced in both countries, as well as, reflecting on some of the essential strategies that the fast food companies have taken to mitigate some of these challenges. The
ultimate area of focus for the comparative study is to examine the overall growth prospects of the fast food industry in both countries as a way of trying to build a front from which to reflect on the similarities and differences.
1.3 Research Objectives
The following are the research objectives for this comparative study.
• To study the influence of the cultural difference between the UK and China on the fast food industry
• To evaluate the different marketing strategies structured by the fast-food organizations for growing the profits in the UK and China
• To suggest the essential cross-cultural model to organizations for improving the performance in the two countries
Based on these research objectives, it is clear that the comparative study will seek to examine the existing cultural differentiation occurring within the United Kingdom and China with the specific focus being on the fast food industry. The study will consider how these differences in culture influence the marketing strategies adopted by fast food companies operating in both countries.
1.4 Research Question
The following are the research questions governing this particular comparative study.
1. What are the primary marketing strategies, which are adopted by the global fast-food organizations in the UK and China market to achieve higher market share?
2. What impact does the difference in culture between China and the UK market have on the marketing strategies of the fast-food organization?
3. What are the main factors affecting the success of fast food retailers in Asian (China) and European market (UK) market?
The research questions reflect more on the marketing strategies adopted by global giants in the fast food industry as a way of trying to create that positive impact among consumers in both China and the United Kingdom. The analysis of the marketing strategies will help towards examining how the fast food companies are using marketing as one of their essential approaches towards achieving higher market shares.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
This section will embark on an in-depth analysis of multiple sources to examine the fast food industry in the United Kingdom and in China, which are the primary markets selected for this comparative study. The analysis will help towards highlighting how the industry has grown over the years, as well as, reflecting on some of the challenges that it has encountered as part of its approach to becoming an essential industry. It is necessary to take note of the fact that indeed the fast food industries in the two countries have experienced significant shifts over the years, which is essential to understand and reflect upon. One critical aspect to note is that the study will focus on the two countries separately with the sole focus being towards reflecting on critical factors defining success in each of these markets.
The review of the literature focusing on the fast food industries in China and the United Kingdom will seek to reflect on how companies operating within these industries have been able to advance their respective positions in a bid to meet consumer expectations. In other words, the review will evaluate how consumers tend to view fast food outlets within the two markets. Additionally, this will also seek to understand how fast food companies within the two markets have been able to use marketing in a bid to capture the attention of the consumers with diverse cultures. In overall, this is expected to pave the way for a prospective position from which to ensure that indeed readers can take note of the existing differences and similarities regarding fast food operations in the two countries.
2.1 Fast Food Industry of the United Kingdom
An analysis of the fast food industry in the United Kingdom indicates that it is one of the markets with the highest consumption levels for fast food products. The growth in the production results from a situation where more people in the country are turning to fast foods as part of their daily expectations towards meeting their expected demands for food products. One of the notable categories of fast foods that have experienced a significant need within the United Kingdom has been the fried chicken and hamburger products. Companies offering these products have undergone a substantial shift regarding their market performance considering that they have been able to capture the attention and demands of consumers in the market. However, it is essential to take note of the fact that the shift in demand for fast food products in the United Kingdom has also been a contributing factor to the growth in this industry.
However, an overview of the fast food industry in the country indicates that the majority of the companies that dominate this industry are international brands, most of which are from the United States. These brands have focused much of their attention towards adopting effective approaches allowing them to advance their positions in the markets as a way of ensuring that indeed they can meet the consumer expectations. The growth in the fast food industry can be seen as a critical strategic position from which to define the position of the United Kingdom when compared to other countries around the world regarding the demand for fast food products.
The following is an in-depth analysis of the fast food industry in the United Kingdom with the focus being towards examining some of the key headlines, trends, evaluation of the
competitive landscape, and highlighting the prospects of the industry. The analysis will seek to explore these elements of the industry in depth as a way of trying to define the viability of this market. The focus in highlighting these elements of the fast food industry in this market is that it would help in providing readers with some sense of understanding on some of the strides that fast food companies have made towards meeting market demands. Additionally, this will also help towards highlighting how the companies, operating within this industry, have been able to capture the attention of the consumers in the market as one of the strategic approaches to building market success.
Headlines of the Fast Food Industry in the UK
According to Wang, Wang, Xue, and Qu (2016, p.1112), more than a quarter of all food outlets within the United Kingdom are fast food restaurants offering a wide array of menus for the varied consumers of the products in the markets. The vast investments by multinational fast food restaurants including KFC, Burger King, and McDonald's has been attributed to the fact that the demand for fast food products is increasing significantly. The demand has increased dramatically especially in areas occupied by the middle class in the economy, who account for approximately 60% of the total fast food products consumed (Gomez and Cheung, 2009, p.153). The British government has been on the forefront towards encouraging investment in the industry, as it has created a leeway through which multinational brands can invest in the country either through franchisees or through direct investment to meet the market demands.
In 2017, the value of the fast food industry in the United Kingdom has grown by a margin of 7% since the early 2000s, which was attributed to the fact that majority of the people in the country appreciate the menus offered in these restaurants (Yu and Titz, 2000, p.39). The value of the fast food industry in 2017 was estimated at £13.5 billion, thus, acting as a clear indication of the fact that indeed this remains as one of the most lucrative industries in the country. Krul and Ho (2017, p.844) argue that the growth in this industry is expected to go higher in coming years considering that the fast food companies are opening new restaurants as a way of capturing more consumers. The opening of new restaurants is seen as a strategic move by the fast food companies to position themselves firmly within the foodservice industry in the UK.
Another critical aspect to take note of when examining the fast food industry in the United Kingdom is the significant increase in the overall number of fast food outlets. As has been stated above, fast food outlets account for more than a quarter of all food service outcomes in the country. Majority of the companies investing in the fast food industry in the UK entered the market after the global recession in 2007. However, the number of outlets has increased by a margin of approximately 13% to 17,294 outlets in different parts of the consumer market (Law, Wu, and Liu, 2014, p.152). The IBIS world has predicted that the fast-food industry will move forward and increase the global economy, as the customers would prefer to spend on eating. Thus, this suggests that indeed the production is expected to experience a significant shift regarding demand for fast food products in the market.
The changing lifestyles among the people living in the United Kingdom have been noted as one of the key factors driving the fast food industry considering that more people are shifting their attention towards intake of a wide array of fast food products. The lifestyle shift has been attributed to an increase in the number of people within the standard level of the economy, thus, creating a situation where people tend to have a higher spending limit. Dastane and Fazlin (2017, p.382) argue that the lifestyle shift among consumers can be seen from the fact that people are spending more on fast food products today than they paid in previous years. The outcome of this is that more people are appreciating the menus offered by the companies investing in the fast food industry in the UK.
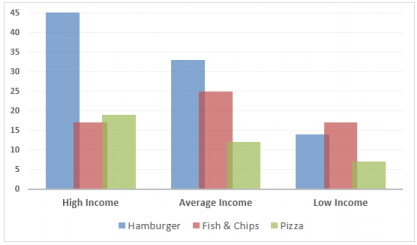
Figure 1: Consumption Levels of Fast Food Products among Different Classes in the United Kingdom
Regarding market dominance, it is essential to take note of the fact that the international brands dominate the fast food industry in the United Kingdoms. McDonald's, which is a multinational fast-food company founded in the United States, is the dominant brand in the UK with a market share of approximately 21% (Lam and Qiu Zhang, 2003, p.219). Economists argue that the dominance associated with the international brands is expected to continue over a forecasted period considering that majority of these companies are investing vast sums of money to meet the market demands (Anderson, Appel, Okuda, Brown, Chan, Zhao, Ueshima, Kesteloot, Miura, Curb, and Yoshita, 2010, p.741). One of the critical areas where the companies have invested significantly is in marketing and advertisement with the focus being towards ensuring that indeed more people can get a clear understanding of their market presence. The companies have engaged in in-depth marketing approaches with the sole focus being towards attracting more consumers towards their respective menus.
The dominance of the international brands within this industry has been attributed to the overall levels of convenience brought about by the companies investing in this industry. Rosenheck (2008, p.537) argues that the international companies investing in the fast food industry within the United Kingdom have introduced menus that are simplified and cost effective. The critical point of fast food outlets is that they need to ensure that the lists remain pure for the consumers allowing them to order in a much more effective manner. On the area of
pricing, fast food products are priced at much lower costs when compared to other food products offered by a majority of other restaurants in the markets, thus, attracting more consumers.
Before their investment in the United Kingdom, the international brands such as McDonalds and KFC have focused on building their prospective positions in the United States, thus, allowing them to understand the overall prospects of the consumer markets (Nguyen, Q.,
Nisar, T.M., Knox, D. and Prabhakar, G.P., 2018, p.1211). The ultimate result of this is that indeed this has played a central role towards ensuring that the companies can use the same approaches that they apply within the United States in a bid to capturing the consumer market in the UK. Additionally, the experience from the United States market has created an effective avenue from which the international brands can build their respective products to match the demands of individual consumers.
According to Williams (2015, p.465), the forecasted growth rate for the fast food industry in the United Kingdom is 4% annually over the next ten years considering that the companies ought to consider the fact that indeed consumers are becoming more health conscious. The fact that consumers are becoming more health conscious means that the number of people consuming fast food products is expected to remain at a constant level regardless of the differentiated approaches taken by the fast food companies (Chiang and Chathoth, 2013, p.218). However, it is essential to consider the fact that indeed more and more people appreciate the fast food products offered by different companies attributed to the convenience and pricing of the products. Thus, this means that more people are expected to consume fast food products in the coming years.
Trends in the Fast Food Industry in the United Kingdom
The first notable trend associated with the fast food industry in the United Kingdom is the fact that although the country has experienced an economic turmoil especially after its exit from the European Union (Brexit), fast food companies have continued to record substantial profit margins. Companies such as Nando’s, which is a fast food brand from South Africa, have filed constant profit margins of between 9% and 12% since Brexit (Bai, Ma, Yang, Zhao, and Gong, 2007, p.1110). Thus, this acts as a clear indication of the fact that indeed consumers of fast food products in the United Kingdom are maintaining their demand for these products regardless of the economic shifts. The influence of the fast food companies in the food service industry is being felt considering that these companies are creating a significant change concerning consumer demand levels for differentiated food products.
The continued growth of the fast food industry in the United Kingdom has also resulted in the introduction of a new concept described as ‘fast casual,’ which is a combination of fast food and full-service restaurants (Zhang, van der Lans, and Dagevos, 2012, p.89). The introduction of this concept has created a position where consumers can order foods that would otherwise be considered in full-service restaurants within fast food outlets. An exam can be seen in the introduction of products such as Crust Gourmet Pizza and Pizza Capers, which are comprised of different ingredients used in the full-service restaurants. The critical element of focus for the fast food outlets is to create an effective avenue from which to build a significant change in the demands among consumers of different fast food products.
On the other hand, it is essential to take note of the fact that fast food outlets are focusing their attention towards creating what would be described as an ‘authentic' atmosphere for consumers of different fast food products. The creation of an ‘authentic' atmosphere seeks to ensure that more people can appreciate fast food products as a way of increasing the demand for the same. Additionally, this is expected to create a front from which fast food companies can build their respective platforms for advanced performance regarding meeting consumer demands. Royle, (2005, p.54)argues that innovation has been a key element of focus for fast food outlets allowing them to focus on what would be described as a revolutionary shift in demands among consumers for different fast food products. By creating an ‘authentic’ atmosphere, the fast food outlets remain guaranteed of an increased number of customers and consumers of different products offered on the menus.
The primary approach adopted by a majority of the international fast food companies in their entry into the United Kingdom market has been franchising with the focus being towards licensing the use of specific brands. Franchising has explicitly been viable for companies intending to advance their market positions by investing in different parts of the Chinese market considering that it allows them to reflect on the differentiated market approaches for the various franchises. On the other hand, franchising creates a front from which companies operating within the fast food industry can gain an in-depth understanding of the differentiated demands among consumers of fast food products (Lang, 1999, p.179). Ultimately, this paves the way for an overall possibility of ensuring that indeed the companies can meet their respective objectives regarding market performance.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the fast food industry within the United Kingdom indicates that majority of the firms competing within this industry are foreign companies from the United States. McDonald's, being on the biggest fast food outlet in the UK, maintains a high level of competitive advantage through its multiple locations in the country making it one of the companies with the highest number of outlets. On the other hand, McDonald's has also been able to build its competitive advantage in the country through its ability to engage in the in-depth marketing of its products as a way of ensuring that it projects that positive outcome regarding performance expectations (Watson, 2008, p.422). However, the company has faced fierce competition from other international brands including KFC, Pizza Hut, and Burger King.
The entry of international brands into the fast food industry in the United Kingdom has been viewed as one of the critical aspects that have helped towards changing the dynamics of the industry significantly. One key example of a changing dynamic is the fact that the fast food industry in the country can meet international standards set out in other countries including the United States and other parts of Europe (Esmaeilpour, Mohamadi, and Rajabi, 2016, p.37). In overall, this is seen as one of the proposed avenues from which the fast food industry in the country can build itself towards becoming one of the most significant and lucrative industries in the world. However, the fact that a substantial number of companies competing within this market are foreign has impacted local investment in the fast food industry, as it has become somewhat challenging for local investors to match the investments by international brands.
The consumer market in the United Kingdom is comprised of approximately 2.5 million consumers of different fast food products with a significant number of these consumers having particular demands regarding the products that the consumer. That has created a situation where the international brands operating in the country have been forced to engage in regular market researches aimed at examining the shifting demands among consumers. In 2015, Subway, which is one of the international brands operating in the UK fast food industry, embarked on a market research process to determine the specific fast foods that consumers expect from such brands (Alnassar, 2017, p.27). The outcome of this market survey has helped the company in building its market position especially in the broader London area, which is one of the biggest markets within the United Kingdom.
The dominance of the international brands also reflects on the fact that a significant number of the fast food outlets are controlled or managed by the global brands attributed to the significant investments that they are making in the country (Kim and Zapata Ramos, 2018, p.124). However, some of the smaller independent fish and chips outlets, which are locally owned, also operate within this consumer market. Most of these smaller outlets offer fast food products that include fish, chips, burgers, and kebab among others. The demand for these products is reducing significantly, as a significant number of consumers are shifting their focus towards international brands attributed to the enhanced quality of products that they offer as part of their abilities to meet market demands (Hosseinzadeh, Abtahi, and Nourbakhsh, 2014, p.441). From a general perspective, it is clear that the smaller shops have experienced significant
challenges in competing with, the broader international brands considering that their investment levels are somewhat limited.
As part of its regulation of the competitive landscape in the fast food industry, the British government has set out specific expectations for companies intending to invest in this industry. The focus of the government has been towards ensuring that it creates an avenue from which to avoid low quality of products delivered to consumers (Thomadsen, 2007, p.802). The local authorities tend to limit the number of restaurants of a specific type, which, in turn, creates a situation where it becomes difficult for companies investing in the fast food industry to operate a high number of outlets. The outcome of this is that it has helped towards paving the way for customer loyalty considering that customers find themselves in a position where they are limited to specific fast food outlets (Anderson and Mirosa, 2014, 829).
Future Prospect of the Fast Food Industry in the United Kingdom
The leading prospect to consider when evaluating the fast food industry in the United Kingdom is the fact that international brands have committed themselves to further investment in the country. The overall demand for fast food products in the United Kingdom is increasing at a significant rate, which acts as a clear indication of the prospects that would be associated with this industry in the country (Lee, Kim, Hemmington, and Yun, 2004, p.81). It is expected that the majority of the international brands of fast food outlets would advance their investment levels with the focus being towards ensuring that indeed they can meet the particular market demands.
The advancements in investments would help pave the way for the United Kingdom's fast food industry to grow at par with the industries in other developed countries.
On the other hand, the lifestyle changes among consumers are also expected to serve as one of the critical elements of focus for any company investing in this fast food market considering that this would translate to a higher revenue platform. Changes in lifestyle demands among consumers mean that consumers would be willing to spend more in a bid to ensuring that indeed they can get what they expect regarding a wide variety of fast food products (Dundes and Swann, 2008, p.158). Fast food outlets ought to take advantage of this by introducing healthier options of fast foods as a way of ensuring that indeed the consumers remain loyal to these brands. The fact that more consumers are becoming health conscious means that the fast food outlets have a crucial role in trying to meet this new demand among fast-food consumers.
More and more reports have cited fast food products as being some of the key factors contributing to increased health conditions affecting significant populations around the world. For the consumers in the United Kingdom, this is one of the critical challenges that they consider in their bid to consuming more fast food products considering that they tend to believe that their consumption of these foods is much more likely to contribute to adverse health (Gilbert, Veloutsou, Goode, and Moutinho, 2004, p.380). Thus, this highlights the prospect of the fast food industry in the United Kingdom towards ensuring that the companies focus on healthier operations. The fast-food outlets must work towards providing their consumers with a guarantee of health as a way of ensuring that indeed the demand for their products increases significantly.
Another critical prospect that fast food companies operating within the United Kingdom ought to consider revolves around the changing demands of consumers regarding the products that they consume. The introduction of new products acts as one of the strategic approaches from fast food companies to advance their positions in a bid to ensuring that indeed they can capture the attention of the consumers (Ming, Ismail, and Rasiah, 2011, p.74). However, this would depend wholly on whether the companies understand the changing demands among consumers, as this would act as a clear indication of the fact that indeed they are building prospective platforms for advanced market performance. Thus, this serves as a clear reflection of the need for having to engage with the consumers as a way of trying to understand their shifting expectations.
2.2 Fast Food Industry in China
The analysis of the fast food in China would focus on providing a background of the industry, as well as, with the focus being towards examining how the industry has been able to build itself over the years. Additionally, the analysis will also seek to provide an overview of the fast food industry over the year as a way of trying to examine how this industry has shifted since the introduction of the modern fast food industry in China. The industry analysis will also seek to examine significant players, as well as, a market composition in the fast food industry within the Chinese market to determine how companies engage in competition. The other areas would consider would include the growth of the industry, future growth of the industry, and critical factors that have contributed to the growth of the sector.
In recent years, the fast food industry in China has experienced a significant shift regarding demand for fast food products attributed to lifestyle changes, as well as, reduced leisure time among consumers in the country. Consumers find themselves spending less time engaging in leisure activities while spending much of their time involved in other activities, thus, paving the way for a huge demand for fast food products in the country. The outcome of this is that consumers are shifting from full-service restaurants towards fast food restaurants as a way of ensuring that they can get food service quicker (Sussan and Kassira, 2009, p.233). That has paved the way for a situation where a majority of the international brands in the fast food industry are entering the Chinese market attributed to the overall prospects of the industry.
On the other hand, it must be noted that influence from the western countries has also been pointed out as a critical factor contributing to the high demand for fast food products. Fast food outlets were developed in the West with countries such as the United States and Canada enjoying a significant platform for fast food companies. However, western influence on the east, especially in China, has created a situation where more people in China are finding themselves in a case where they demand more fast food products. Thus, this has been of great value towards creating a significant shift regarding fast food expectations within the Chinese market with the focus being towards ensuring that indeed consumers can emulate the western countries. In overall, this has also played a key role towards attracting more international brands into the Chinese market, as a way of advancing their investments.
According to the 2018 projections for the fast food industry in China, the production is expected to generate $174.73 billion, which will be an increase of 10.7% from 2017. The projections also indicate that the annualized rate of growth in the industry is moving at a constant rate of 11.1%. The fast-food industry in China has experienced significant growth attributed to the fact that the number of fast food outlets in the country is increasing significantly especially in regions where the demand for these products is high. Currently, there are approximately 2.3 million fast food restaurants in the Chinese market out of which 55.4% are controlled and operated by international brands such as KFC and McDonalds. The significant number of outlets in the country can be attributed to the considerable population growth experienced in the country within the last decade.
An in-depth analysis of the fast food industry in China indicates that it is poised towards becoming one of the leading sub-sectors of the economy while taking into account the impacts that it is expected to have on the economy. The economic consequences will not only focus on the fact that more people are demanding more fast food products but also from the point that these companies are offering essential platforms for employment. An example can be seen from Yum, which is a brand that licenses the fast food outlet KFC. Yum is one of the largest brands of fast food outlets in China operating over 100,000 stores with an employee base of over half a million people. Thus, this seems to suggest that indeed the fast food industry is expected to create that prospective avenue from which to advance overall capacities for economic development.
The entry of fast food companies into the Chinese market has been viewed as one of the strategic efforts for China towards improving multiple areas that include chain store and franchising management as two key areas expected to advance business performance. That can be seen from the fact that the international brands have introduced the concept of franchising within the Chinese market. Most of the fast food outlets that have global branding in the Chinese market are franchises that have been given the license to operate from the original companies themselves (Cheng, Chiu, Hu, and Chang, 2011, p.5122). Thus, this has created an avenue from which companies can build or define their respective capacities in ensuring that they can develop or maintain that prospective avenue for advanced business performance. In overall, this has been seen as a critical aspect from which to provide that indeed businesses in the Chinese market can improve on their capacities to achieve set out goals.
Overview of the Fast Food Industry in China
The modern fast food industry in China can be traced back to 1987 during which time KFC opened its first outlet not only in China but also in the entire of Asia (He, Brinsden, and MacGregor, 2014, p.345). The opening of this outlet was viewed as one of the strategic efforts of the company in trying to create new markets around the world. Additionally, this was considered as one of the critical approaches by an international brand in deciding to introduce the fast-food concept into new regions around the world as a way of creating or promoting demand for fast food products.
Over the next two decade, the country has experienced a significant shift regarding demands for fast food products considering that more people in the Chinese market have been introduced into the idea of fast food. The industry has experienced a significant change considering that the number of international brands that have invested in this market has increased significantly, as well as, the fact that the demand for fast food products is growing dramatically (Pingali, 2007, p.292). This period also created that prospective avenue from which consumers can get a clear understanding of the meaning of fast food products with the focus being towards ensuring that more people can appreciate these products. In overall, this has been seen as a critical period in the fast food industry in China considering that it has helped in the redefining of the market as a way of advancing their overall prospects of the sector towards becoming one of the leading subsectors of the economy.
The adoption of fast food outlets has been seen from the perspective that majority of these outlets tend to focus on creating what would be considered as Chinese-style facilities with the sole focus being towards appealing for the Chinese consumers (Hawkes, 2007, p.1969). Chinese consumers are regarded as being very culturally conscious especially when it comes to issues of restaurants, as they tend to focus on restaurants that would allow them to connect to their Chinese culture. In overall, this is seen as one of the critical aspects that have helped towards ensuring that indeed fast food industry in China experiences a significant shift regarding demand for multiple fast food products.
The rapid growth in the fast food industry in China has been attributed to several key factors, which include early development of the Chinese economic structure, changes in social norms, increased income levels within families, and urbanization (Popkin, 2008, p.1072). These factors have created a situation where Chinese consumers tend to find themselves in a position where they tend to view themselves within the perspective of the western culture. Ultimately, this has been of great value towards ensuring that indeed these consumers can appreciate the overall existence of fast food outlets in the country as a way of meeting prospective expectations (Liu, Xie, Chou, Koprowski, Zhou, Palmer, Sun, Guo, Duan, Sun, and Johnson, 2007, p.751). The demand can be seen from the fact that the fast food industry has experienced a significant shift regarding increasing revenue outcomes from the industry.
Market Composition of the Fast Food Industry in China
An in-depth review of the fast food industry indicates that approximately 76% of the industry is privately owned with the rest being state owned. Most of the private companies that have invested in the Chinese market are American corporations taking into account that majority of the international brands of fast food companies are from the United States, which is one of the countries with the highest number of fast food brands. China is a communist state meaning that the government controls a significant part of the economic structure in the country (Ambler Edwards, Bailey, Kiff, Lang, Lee, Marsden, Simons, and Tibbs, 2009, p.10). However, this is not the case in China considering that majority of the fast food outlets in the country are privately
owned, thus, paving the way for foreign investment in the industry as a way of ensuring that indeed the industry would be able to build itself effectively.
The largest foreign brand in the Chinese fast food industry is KFC, which operates in more than 1,000 cities and towns in the country with the focus being towards ensuring that the brand can deliver on expected demands among consumers. KFC operates in all provinces within the Chinese market except for the Province of Tibet (Maxwell and Slater, 2003, p.549). The second largest foreign brand operating in the fast food industry in China is McDonald's. McDonald's opened its first outlet in China back in 1990 with the focus being towards expanding from the traditional American market. The entry of McDonald's in the Chinese market was viewed as one of the critical pointers towards defining an overall shift in the industry considering that the company sought to create a front from which to compete with its international rival KFC for the Chinese consumer market share.
It is equally important to take note of the fact that domestic style fast food outlets in China have also expanded with the primary influence being attributed to the entry of the western brands into the Chinese market. The largest domestic fast food outlet in China is Malan Noodle, which was founded back in 1995 but remains smaller when compared to a majority of the western brands (Frazão, Meade, and Regmi, 2008, p.24). By 2008, Malan Noodles was operating approximately 400 outlets in the Chinese market, which was viewed as being less competitive in trying to meet the demands among the Chinese consumers. On the other hand, the Chinese fast food industry is also comprised of Chinese-style rice sets, which also seek to offer quick service
to consumers. These fast food outlets account for approximately 33.4% of the total revenue associated with the fast food industry in the Chinese market.
The growth of Chinese Fast Food Industry
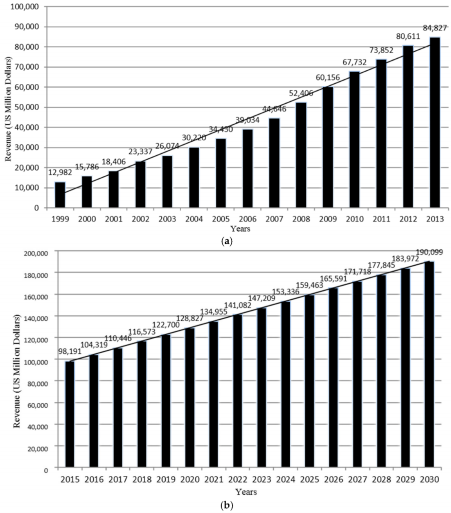
To help in examining the growth of the Chinese fast food industry, one must take note of the revenue increase from this industry since 1999, as well as, review the projected increase in future (as has been presented in figure 2) (Veeck and Burns, 2005, p.649). The entry of the American fast food companies has been viewed as one of the strategic elements that have helped towards ensuring that indeed the industry can achieve the expected growth margin. The American brands have contributed towards improving on the management of the sector with the focus being towards ensuring that indeed the industry can experience a significant shift regarding overall capacities to deliver on set out prospects. Thus, this has created a situation where the demand for fast food products has increased significantly since the 1990s.
The entry of some of the reliable brands such as McDonalds and KFC has been considered as one of the critical elements that have contributed to the significant growth experienced in the fast food industry in the country. Before their entry into the Chinese market, the international brands had been able to build their positions within the fast food industries in other countries such as the United States among other developed countries (Schrempf, 2014, p.316). These brands have not only positioned in the Chinese market but have set out effective approaches including engaging in marketing with the focus being towards attracting more consumers towards fast food products. The American brands find themselves in a position where
they are expected to operate within a new cultural environment, thus, creating the need for them to enhance their respective capacities towards meeting demands among consumers (Ambler, 2006, p.145).
Figure 2: Trends in Fast Food Industry Revenue Growth and Future Projection in China between 1999 and 2030
Alternatively, the growth in the Chinese fast food industry has been attributed to the intensified competitive environment created by international brands, which, in turn, has built a significant challenge for local Chinese restaurants. That has created a situation where a majority of these restaurants have focused much of their attention towards creating new products that would allow them to capture the attention of consumers within the Chinese market (Fraser, Edwards, Cade, and Clarke, 2011, p.1325). The competitive environment created has also been of great value towards stimulating performance in the Chinese market, as it has become essential for companies to build their respective positions based on the quality of products that they offer.
The international brands have operated in environments where quality expectations are significant in protecting the consumers of fast food products. Their entry into the Chinese market helped towards creating that prospective avenue from which to ensure that the local Chinese fast food outlets advance the quality of the products that they offer. Additionally, the marketing approaches that the western companies have adopted focus more on reaching out to adolescents and young adults as part of increasing demand for a wide array of fast food products. The long term outcome of this is that the brands have been able to create a significant shift regarding capacity to meet set out goals and objectives while ensuring that indeed consumers appreciate the fast food products offered within the consumer markets (McMichael, 2000, p.27). That has worked as one of the critical factors that have prompted an overall growth in the Chinese fast food industry towards becoming one of the most lucrative subsectors.
The success outcomes for the majority of international brands within the Chinese market may catalyze ensuring that the industry maintains prospective performance in future taking into account that this would work as an avenue from which to define the industry. That means that the success of the fast food industry in China is limited to the levels of success that international brands may have within the industry in this country (Yan, 2012, p.717). Analysts argue that the Chinese government ought to encourage more investment into the Chinese fast food industry with the focus being towards ensuring that more investors would create fast food outlets that would be viewed as critical platforms from which to increase demands for fast food products in the country.
Another key aspect to note is that lifestyle changes have also been considered as one of the key factors contributing to the growth of the fast food industry in the Chinese society. The fact that China has developed towards becoming one of the largest economies in the world has paved the way for a faster pace regarding work and life. Thus, this has paved the way for lifestyle changes considering that more people find themselves spending more of their time working and having limited time to eat. Fast food outlets serve as notable alternatives considering that they help in reducing the time taken in food service while ensuring that indeed consumers of these foods have adequate time to undertake other duties.
The fact that fast food restaurants are introducing new types of products depending on taste preference and cost may serve as one of the critical elements to consider in defining the overall possibilities of increasing demand fast food products. Taste preference is a vital
expectation in ensuring that indeed consumers can get foods that match their particular taste expectations while providing that indeed they can meet their respective costs. Majority of the fast food companies operating within the Chinese fast food industry have been able to create a front from which to build this position where the focus is towards advancing a specific location from which people would appreciate fast food products. The fast-food outlets have also focused much of their attention towards creating that comparative platform from which to ensure that the number of people expected to appreciate these foods increases significantly as a way of meeting set objectives in the market.
Lastly, the growth of the industry can be attributed to overall shifts in social norms with more people appreciating the fact that they can eat out more often than usual. China is one of the societies that acknowledge the family unit. Thus, most of the people in China had developed the social norm allowing them to eat at home most of the time. However, this is fast changing considering that more people are appreciating the fact that indeed fast food outlets are becoming social norms within the Chinese society. The outcome of this is that the people are focusing much of their attention towards eating out as a way of appreciating the overall changes in social norms and expectations within the Chinese social setting.
Factors Contributing to the Growth of the Industry
The following is an overview of some of the critical elements that have been of great value towards ensuring that the Chinese fast food industry achieves the expected growth margins.
1. Large Population Size
China is one of the most populous countries in the world with a population of over 1.3 billion people (Vu, Chan, Lim, and Chiu, 2017, p.1047). Thus, this acts as a critical front from which to ensure that the country can build itself as a vital market for fast food companies with the sole focus being towards providing that indeed companies can meet their prospective expectation. The fact that the Chinese population is increasing at a rapid rate has created a potential avenue from which to ensure that indeed companies operating within the fast food industry build their respective positions. From an overall perspective, the population in China has been viewed as one of the critical drivers defining the growth of the Chinese fast food industry.
2. Popularity and Peer Influence
The popularity of fast food outlets and brands has been considered as one of the critical aspects of focus towards defining the overall shift regarding demand for fast food products. Majority of the international brands operating within the Chinese market have engaged in in depth marketing and advertisement of their products with the focus being towards ensuring that indeed they can reach a more significant consumer platform (Wang, Royo Vela, and Tyler, 2008, p.322). On the other hand, influence among adolescents and young adults to take up fast food products are viewed as another critical factor contributing to the increasing demand for fast food products in the Chinese market.
3. Health Consciousness and Food Safety Concerns
Fast foods outlets have been noted as having understood the importance of maintaining the highest food safety standards. Thus, this has created a situation where a majority of the consumers of foods within the food service industry are focusing much of their attention toward fast food outlets when compared to smaller restaurants. The consumers tend to believe in the fact that these outlets offer a better position regarding ensuring that they deliver foods that maintain the highest standards regarding quality (Cheng, and Wong, 2015, p.129). However, the consideration of the impacts associated with fast foods may act as a key source of concern, as this is much more likely to create a significant reduction in demand for fast foods products.
Future Growth of the Chinese Fast Food Industry
The growth potential of the fast food industry in China can be viewed from the perspective that more people are demanding for fast food products, as well as, the fact that fast foods are offer favorable pricing. Zhao, Wang, Xue, Wang, and Wang (2017, p.933) indicate that the projected growth of the fast food industry in China between 2008 and 2018 was between 10.7% but experienced a constant growth pattern of 11.1%. Thus, this acts as a clear indication of the fact that indeed the fast food industry is shifting much of its focus towards ensuring that more people would appreciate the overall structure of the industry. Additionally, this means that more people would be willing to take fast food products rather than having to focus on full service restaurants, which are reducing in number within the Chinese consumer market.
The future growth of the fast food industry in China can also be viewed from the perspective that China's economy is growing at an average rate of 8.0% annually. Thus, this means that the Chinese population is experiencing a significant increase in income levels, therefore, paving the way for a considerable shift regarding overall capacities to deliver on set out expectations (Wu, and Mohi, 2015, p.379). The fact that the Chinese economy is improving means that the people in China would be willing to spend more money on fast foods, thus, acting as one of the critical elements of consideration in trying to define the overall prospects of the fast food industry in the country. That has been the same case in other countries such as the United States considering that the growth in the fast food industry has been proportional with the increase in economic prospects of the country meaning that people have a higher disposable income.
3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research methodology in the fast food industry requires the implementation of appropriate data collection methods that help in obtaining reliable and relevant information regarding the industry. In this study, the research methodology focused on data collection and analysis techniques that helped in making a proper comparison of the fast food industry of China and the United Kingdom. The data collected from collection methods helped in testing the hypotheses presented in the research to ascertain the reliability of the received information. Considering the nature of the fast food industry, the study focused on the implementation of data collection methods that would help in obtaining accurate information regarding the trends and factors influencing the growth of the sector in China and the UK. The research focused on the use of methodologies that would be suitable for all participants from China and the UK to capitalize on enhancing positive results that help in making an appropriate comparison.
3.1 Data Collection
The first data collection methods used in this study involved the use of questionnaires to obtain the required information from the selected participants. The purpose of inquiries in the research focused on achieving results regarding facts, trends, and other factors associated with the fast foods industry in the UK and China. The use of questionnaires helps in the collection of primary data, which enables the researcher to obtain reliable and appropriate information regarding the research questions. In this case, the issue of comparing the fast food industry of China and the United Kingdom required the researcher to obtain primary information concerning
the two sector to make a proper comparison on the crucial factors that influence growth and development of the industry. The questionnaires served as a vital tool that would help in reaching out to a wide range of participants that would take part in the research and be in a position to present their thoughts regarding the fast food industry.
The decision to use data collection technique as a primary method of obtaining data from the participants has various advantages that make it more preferred than other data collection methods. The first advantage associated with the use of questionnaires for this research involved the affordability associated with the use of the data collection technique. Using the given data collection technique, the researcher was in a position to reach out to a wide range of participants effectively without incurring extra costs associated with obtaining data from the research respondents. The second advantage associated with the use of questionnaires in this study involved the provision of an opportunity for the researcher to introduce the topic to the participants for them to understand the actual issues that are addressed within the research. Ensuring that the participants have an understanding of the requirements of the study helps in enhancing the responses thus increasing the reliability and credibility of the collected information. Lastly, the use of questionnaires provided the researcher with the ability to collect responses within a short period considering filling out the surveys is perceived to be a simple exercise.
To capitalize on enhancing effectiveness in the data collection exercise through the use of questionnaires, the researcher focused on proper structuring of the questions as part of
undertaking adequate designing of the questionnaires. The first element in the structure of the questionnaires involved the use of open and close-ended questionnaires that focused on obtaining a different type of data from the participants concerning understanding the fast-food industry of China and the UK. The open questions within the questionnaires sought to obtain an opinion regarding issues such as growth and development of the industry, trends, and the future of the industry in both regions. Additionally, the open questions provided an avenue for making proper comparisons of the industry based on personal opinion and the based on the factual elements that relate to the industry. The questionnaires were designed into sections that presented different dimensions regarding the fast food industry such as the service quality, the quality of food, customer satisfaction, perceived value, and the behavioral aspects that contribute to the purchase intentions of the fast foods in both China and in the United Kingdom.
The second data collection technique implemented for the collection of data regarding the research topic included the use of secondary sources. The researcher capitalized on the use of magazines, websites, and books, to obtain information that concern the fast foods industry. The use of secondary sources in this research was necessary to obtain information regarding the history of the industry in China and the UK and understand factors that have influenced the growth and development of the industry over the years. The secondary sources helped in the provision of comparison data from previous researches, which is an aspect that assisted the researcher in making proper conclusions based on the given information. Additionally, this data collection method provided a platform for obtaining statistical information regarding the growth
of the industry in China and the United Kingdom thus allowing the researcher to have factual information that is helpful to confirm and test the hypotheses developed for the study.
The decision to use the data collection method in the research was attributed to a number of facts, which included the nature of data required for the completion of the study to allow the researcher to make proper conclusions regarding how the fast food industry of China compares to that of the United Kingdom. The second aspect concerning the decision to use the data collection techniques involved the affordability of the method considering that most of the materials that were intended to be used in the research were readily available for the researcher to access. The third advantage associated with the use of the secondary data method techniques involved the aspect of saving research period considering that the researcher did not have to spend time finding participants to take part in the study. Lastly, the data collection n techniques provided reliable and appropriate information, which was valid for the given research considering that the data had been previously collected and evaluated before being stored in the secondary sources.
The third method used in the collection of data in this study involved the use of interviews. Interviews are an essential data collection method that helps in obtaining primary and firsthand information from the respondents without issues such as bias. The use of interviews in the collection of data provides an avenue for verbal communication between the interviewer and the interviews, which is an aspect that helps in the obtaining actual reactions and personal thoughts through the interaction. The researcher focused on ensuring that the interviews provided
an opportunity to collect critical information concerning the factors that influence the buying behaviors of individuals in the fast food industry. Through the interviews, the researcher was in a position to understand individual factors that contribute to the growth and development of the industry in both China and in the United Kingdom. The researcher ensured that the interview questions presented were precise focusing on the goals and objectives of the study to capitalize on obtaining relevant information that is helpful in making relevant conclusions.
The implementation of the three data collection techniques in the study focused on the achievement of the research goals and objectives that were part of making relevant comparisons regarding the fast foods industry in China and the UK. To come up with the appropriate data collection methods, the researcher focused on understanding the nature of information required for the completion of the given research to identify the most appropriate methods that would be in a position to provide relevant and accurate data. The researcher focused on analyzing the participants that were intended to take part in the research to identify the most appropriate data collection technique that would suit them. This is because the research was an extensive study that required reaching out to fast foods industry in China and the United Kingdom. Additionally, the researcher capitalized on identifying the research goals and objectives by formulating research questions and hypotheses that would assist in the process of obtaining appropriate information concerning the fast food industry.
3.2 Data Analysis
In this study, data analysis was an important aspect that helped in enhancing the rehabilitee and validity of the information collected from various sources during the collection process. The researcher capitalized on the implementation of analysis techniques that would help in ensuring that the information obtained is used to make the relevant conclusions regarding how the fast food industry in China compares to the industry in the United Kingdom. The analysis process involved the elimination of unreliable and inappropriate data the through the process of arranging and transforming the data into more meaningful information that is easy to interpret. Considering that the researcher implemented the use of various data collection techniques, the analysis tools used were different for each type of data to capitalize on enhancing the reliability and appropriateness of the information. The analysis process helped in making proper summaries by making proper descriptions of the observations obtained from the study.
The first analysis technique implemented by the researcher involved the use of Pearson Correlation. The Pearson Correlation technique is used in research to describe a relationship that exists between two variables, which are identified in the research. The analysis technique capitalizes on the use of linear fashion approach during the process of describing how various variables relate. In this case, the researcher implemented the use of the technique to create a significant comparison between the fast food industry in China and the United Kingdom. Using the technique, the researcher was able to identify various factors that influence the growth and
development of the industry in both China and the UK, by undertaking analysis on the significant responses obtained from the participants undertaking the study.
The second techniques used by the researcher in undertaking the analysis process involved the use of Hierarchical Multiple Regression. Hierarchical Multiple Regression is a technique that helps in examining the mediating effect between various variables used in the research. In this case, the researcher capitalized on making relevant considerations regarding the technique based on the independent variables identified in the research. The first criterion used during the analysis involved the aspect of the independent variables being significantly associated with the mediator. The second criterion considered that the independent variable was significantly associated with the dependent variable. The provisions within the mentioned criteria assisted the researcher in arranging the collected data into a more useful and relevant data that would be used in making relevant conclusions. Through the Hierarchical Multiple Regression techniques, the researcher was able to identify various aspects associated with the fast food industry such as the purchasing behavior of the customers, which plays a significant role in defining the future of the industry.
3.3 Research Philosophy
A research philosophy entails the summaries of research experiences and interests that are defined by the individual beliefs regarding how the research process should be undertaken in a bid to capitalize on positive results. The beliefs focus on defining data collection and analysis methods that should be used in any given research. The research philosophy that was
implemented by the researcher in this comparative case study will be positivism, which is a philosophical element that helps in defining the processes associated with data collection. The positivism approach focuses on the use of data collection methods that helps in providing a scientific proof concerning an element of the study.
The researcher capitalized on the approach based on the ability to provide evidence of the research concerning the research topic that aims at comparing the fast food industry in China and the UK. Positivists believe in the aspect of stability of reality and that the reality can be observed and described from an individual's point of view without the interference of the issue being
studied. The use of the approach was relevant in the study considering the nature of the issue that was studied in the research, which required the availability of pieces of evidence regarding a given variable. Based on the positivism approach implemented by the researcher in the study, the data collected will be statistical data, which will be assessed in a quantifiable manner to capitalize on authenticating the provided information.
3.4 Research Approach
In this study, the researcher capitalized on the use of deductive and inductive research approaches considering the nature of the information that was required for the completion of the research. The deductive and inductive approaches focus on the construction of a valid argument within the given research based on the collected information. The approaches play a significant role in making undeniable facts within research, which is an aspect that helps in the achievement of the research goals and objectives. The deductive research approach works from a general
perspective into a more specific aspect whereby conclusions follow logically based on the available facts obtained from a given study. The approach undertakes four critical elements that involve the theory, hypotheses, observation, and then finally the confirmation. On the other hand, the inductive research approach works from a more specific aspect into generalized and broader perspectives thus making it the opposite of the deductive approach. In this approach, the conclusions made are based on the premises and involve a high degree of uncertainty based on the results obtained from the study.
3.5 The significance of the Study
The significance of this study can be seen from the fact that it helps in understanding the differentiation regarding marketing approaches that companies ought to take in their bid to engaging in different markets. The analysis seeks to examine how the fast food industries differ from China and the United Kingdom. The focus is on trying to examine how companies intending to invest in these two countries may experience a significant shift regarding their abilities to meet set out objectives. The research is essential in understanding the marketing strategies, which the fast food organizations utilize when they move into the different country which has a different culture. This research also helps in identifying the impact of culture when it comes to fast-food industry and how the change in lifestyle of people has led to a rising in the demand of the fast-food industry products. In overall, this will seek to create that positive front from which to ensure that indeed companies can build their prospective positions as part of their engagement in the fast food industry in both countries.
4. Bibliography
Alnassar, F., 2017. Franchising and the internationalization of businesses: the case of fast food chains. Przedsiębiorczość Międzynarodowa, 3(2), pp.23-36.
Ambler, T., 2006. Does the UK promotion of food and drink to children contribute to their obesity?. International Journal of Advertising, 25(2), pp.137-156.
Ambler-Edwards, S., Bailey, K.S., Kiff, A., Lang, T., Lee, R., Marsden, T.K., Simons, D.W., and Tibbs, H., 2009. Food futures: rethinking the UK strategy. A Chatham House report. Anderson, C., Appel, L., Okuda, N., Brown, I., Chan, Q., Zhao, L., Ueshima, H., Kesteloot, H., Miura, K., Curb, J.D. and Yoshida, K., 2010. Dietary sources of sodium in China, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States, women and men aged 40 to 59 years: the Intermap study. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 110(5), pp.736-745. Anderson, K. and Mirosa, M., 2014. Revealing barriers to healthier fast food consumption choices. British Food Journal, 116(5), pp.821-831.
Bai, L., Ma, C.L., Yang, Y.S., Zhao, S.K. and Gong, S.L., 2007. Implementation of the HACCP system in China: A survey of food enterprises involved. Food Control, 18(9), pp.1108- 1112.
Cheng, C.C., Chiu, S.I., Hu, H.Y. and Chang, Y.Y., 2011. A study on exploring the relationship between customer satisfaction and loyalty in the fast food industry: With relationship inertia as a mediator. African Journal of Business Management, 5(13), pp.5118-5126.
Cheng, S. and Wong, A., 2015. Professionalism: A contemporary interpretation in hospitality industry context. International journal of hospitality management, 50, pp.122-133.
Chiang, J. and Chathoth, P.K., 2013. International expansion strategy of foodservice firms: An exploratory study. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 22(2), pp.204-228. Dastane, O. and Fazlin, I., 2017. Re-Investigating Key Factors of Customer Satisfaction Affecting Customer Retention for Fast Food Industry. International Journal of Management, Accounting & Economics 4(4), pp.379-400.
Dundes, L. and Swann, T., 2008. Food safety in fast food restaurants. Journal of Human Resources in Hospitality & Tourism, 7(2), pp.153-161.
Esmaeilpour, M., Mohammadi, Z., and Rajabi, A., 2016. Effect of dimensions of service quality on the brand equity in the fast food industry. Studies in Business and Economics, 11(3), pp.30-46.
Fraser, L.K., Edwards, K.L., Cade, J.E. and Clarke, G.P., 2011. Fast food, other food choices and body mass index in teenagers in the United Kingdom (ALSPAC): a structural equation modeling approach. International Journal of Obesity, 35(10), p.1325.
Frazão, E., Meade, B. and Regmi, A., 2008. Converging patterns in global food consumption and food delivery systems. Amber Waves, 6(1), pp.22-29.
Gilbert, G.R., Veloutsou, C., Goode, M.M. and Moutinho, L., 2004. Measuring customer satisfaction in the fast food industry: a cross-national approach. Journal of Services Marketing, 18(5), pp.371-383.
Gomez, E.T., and Cheung, G.C., 2009. Family firms, networks and ‘ethnic enterprise’: Chinese food industry in Britain. East Asia, 26(2), pp.133-157.
Hawkes, C., 2007. Regulating and litigating in the public interest: regulating food marketing to young people worldwide: trends and policy drivers. American journal of public health, 97(11), pp.1962-1973.
He, F.J., Brinsden, H.C. and MacGregor, G.A., 2014. Salt reduction in the United Kingdom: a successful experiment in public health. Journal of human hypertension, 28(6), p.345. Hosseinzadeh, M., Abtahi, M., and Nourbakhsh, K., 2014. The role of market orientation on market chaos: A case study fast food industry. Management Science Letters, 4(3), pp.439-442.
Kim, Y. and Zapata Ramos, M.L., 2018. Stakeholder responses toward fast food chains' CSR: Public health-related vs. generic social issue-related CSR initiatives. Corporate Communications: An International Journal, 23(1), pp.117-138.
Krul, K. and Ho, P., 2017. Alternative approaches to food: Community supported agriculture in urban China. Sustainability, 9(5), p.844.
Lam, T. and Qiu Zhang, H., 2003. Job satisfaction and organizational commitment in the Hong Kong fast food industry. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 15(4), pp.214-220.
Lang, T., 1999. The complexities of globalization: The UK as a case study of tensions within the food system and the challenge to food policy. Agriculture and human values, 16(2), pp.169-185.
Law, R., Wu, J. and Liu, J., 2014. Progress in Chinese hotel research: A review of SSCI-listed journals. International journal of hospitality management, 42, pp.144-154.
Lee, S.H., Kim, Y.P., Hemmington, N. and Yun, D.K., 2004. Competitive service quality improvement (CSQI): a case study in the fast‐food industry. Food Service Technology, 4(2), pp.75-84.
Liu, C., Xie, B., Chou, C.P., Koprowski, C., Zhou, D., Palmer, P., Sun, P., Guo, Q., Duan, L., Sun, X. and Johnson, C.A., 2007. Perceived stress, depression and food consumption frequency in the college students of China Seven Cities. Physiology & behavior, 92(4), pp.748-754.
Maxwell, S. and Slater, R., 2003. Food policy old and new. Development policy review, 21(5‐6), pp.531-553.
McMichael, P., 2000. The power of food. Agriculture and human values, 17(1), pp.21-33. Ming, T.T., Ismail, H.B. and Rasiah, D., 2011. Hierarchical chain of consumer-based brand equity: Review from the fast food industry. International Business & Economics Research Journal, 10(9), pp.67-80.
Nguyen, Q., Nisar, T.M., Knox, D. and Prabhakar, G.P., 2018. Understanding customer satisfaction in the UK quick service restaurant industry: The influence of the physical attributes of perceived service quality. British Food Journal, 120(6), pp.1207-1222.
Pingali, P., 2007. Westernization of Asian diets and the transformation of food systems: Implications for research and policy. Food policy, 32(3), pp.281-298.
Popkin, B.M., 2008. Will China’s nutrition transition overwhelm its health care system and slow economic growth?. Health Affairs, 27(4), pp.1064-1076.
Qin, H., Prybutok, V.R., and Zhao, Q., 2010. Perceived service quality in fast-food restaurants: empirical evidence from China. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 27(4), pp.424-437.
Rosenheck, R., 2008. Fast food consumption and increased caloric intake: a systematic review of a trajectory towards weight gain and obesity risk. Obesity Reviews, 9(6), pp.535-547. Royle, T., 2005. Realism or idealism? Corporate social responsibility and the employee stakeholder in the global fast‐food industry. Business Ethics: A European Review, 14(1), pp.42-55.
Schrempf, J., 2014. A social connection approach to corporate responsibility: The case of the fast-food industry and obesity. Business & Society, 53(2), pp.300-332.
Sussan, A.P., and Kassira, R.D., 2009, January. Customization and Technological Change in the Fast Food Industry. In Competition Forum 7(1), pp. 228-233.
Tan, Q., Oriade, A. and Fallon, P., 2014. Service quality and customer satisfaction in Chinese fast food sector: A proposal for CFFRSERV. Advances in Hospitality and Tourism Research (AHTR), 2(1), pp.30-53.
Thomadsen, R., 2007. Product positioning and competition: The role of location in the fast food industry. Marketing Science, 26(6), pp.792-804.
Veeck, A. and Burns, A.C., 2005. Changing tastes: the adoption of new food choices in post reform China. Journal of Business Research, 58(5), pp.644-652.
Vu, H.M., Chan, H.K., Lim, M.K., and Chiu, A.S., 2017. Measuring business sustainability in food service operations: a case study in the fast food industry. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 24(4), pp.1037-1051.
Wang, Y., Royo Vela, M. and Tyler, K., 2008. Cultural perspectives: Chinese perceptions of UK hotel service quality. International Journal of Culture, Tourism and Hospitality Research, 2(4), pp.312-329.
Wang, Y., Wang, L., Xue, H. and Qu, W., 2016. A review of the growth of the fast food industry in China and its potential impact on obesity. International journal of environmental research and public health, 13(11), p.1112.
Watson, S., 2008. A conceptual model for analyzing management development in the hospitality industry: A UK perspective. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 27(3), pp.414-425.
Williams, S.N., 2015. The incursion of ‘Big Food’in middle-income countries: a qualitative documentary case study analysis of the soft drinks industry in China and India. Critical Public Health, 25(4), pp.455-473.
Wu, H.C., and Mohi, Z., 2015. Assessment of service quality in the fast-food restaurant. Journal of Foodservice Business Research, 18(4), pp.358-388.
Yan, Y., 2012. Food safety and social risk in contemporary China. The Journal of Asian Studies, 71(3), pp.705-729.
Yu, Z. and Titz, K., 2000. Franchising opportunities in China for American fast food restaurants. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 5(1), pp.38-46.
Zhang, X., van der Lans, I. and Dagevos, H., 2012. Impacts of fast food and the retail food environment on overweight and obesity in China: a multilevel latent class cluster approach. Public health nutrition, 15(1), pp.88-96.
Zhao, Y., Wang, L., Xue, H., Wang, H. and Wang, Y., 2017. Fast food consumption and its associations with obesity and hypertension among children: results from the baseline data of the Childhood Obesity Study in China Mega-cities. BMC public health, 17(1), p.933.